Table of Contents
Otosclerosis is a condition that affects the bones in the middle ear, particularly the stapes, leading to hearing loss over time. Though it can develop in anyone, it is more common in adults aged 20–50 and is often linked to hereditary ear disease.
People with otosclerosis may notice gradual hearing loss, difficulty understanding conversations in noisy environments, or ringing in the ears. Understanding this condition, recognizing early otosclerosis symptoms, and knowing the available treatments, including otosclerosis surgery, is essential for preserving hearing and quality of life.
Anatomy of the Ear and How Otosclerosis Develops
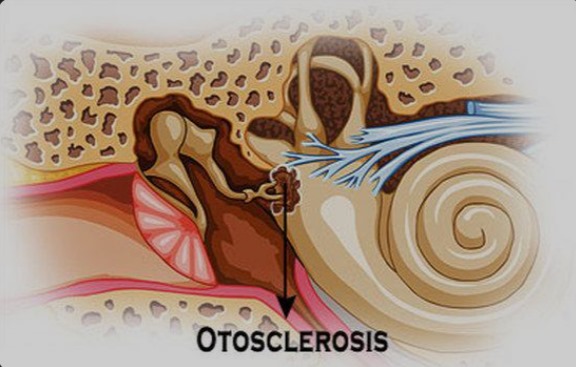
The ear consists of three parts: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. The middle ear contains three small bones—the malleus, incus, and stapes—which transmit sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear.
In otosclerosis, abnormal bone growth occurs around the stapes, causing it to become fixed in place (stapes fixation). This prevents proper movement, disrupting sound transmission and resulting in bone hearing loss. Over time, if left untreated, the condition can worsen, affecting both ears in many cases.
The condition is believed to have a hereditary component, often passing through families, which is why early screening in relatives of affected individuals may be recommended.
Common Otosclerosis Symptoms
Recognizing otosclerosis symptoms early can help in timely intervention. Common signs include:
- Gradual hearing loss, often starting in one ear
Hearing may slowly decline over months or years, often affecting one ear first before progressing to both. Early detection allows for better treatment outcomes. - Difficulty hearing low-pitched sounds
Sounds like voices, music, or environmental noises may become muffled, making conversations challenging, especially in quiet settings. - Trouble understanding speech in noisy environments
Background noise can make it harder to focus on conversations, leading to frustration and social withdrawal if untreated. - Ringing or buzzing in the ears (tinnitus)
Tinnitus can vary from a soft background noise to persistent ringing, sometimes worsening during periods of stress or fatigue. - Occasional dizziness or balance issues
While less common, some individuals may experience mild balance disturbances if the inner ear is affected, adding to the overall discomfort.
If you experience these symptoms, a hearing evaluation through pure tone audiometry or ABR/ASSR testing, can confirm the diagnosis and measure the degree of hearing loss.
Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact cause of otosclerosis is not fully understood, research points to several factors:
- Genetic Predisposition: A strong link with hereditary ear disease has been observed.
- Hormonal Factors: Women may experience progression during pregnancy.
- Viral Infections: Measles infection has been linked to abnormal bone growth in the ear.
- Age: Most cases develop in early adulthood.
Understanding these risk factors helps in identifying those who may benefit from early screening and preventive measures.
Types of Hearing Loss in Otosclerosis
Otosclerosis typically causes conductive hearing loss, where sound vibrations are blocked by the immobile stapes. However, in some cases, sensorineural hearing loss may occur if the inner ear is affected.
- Conductive Hearing Loss: Caused by stapes fixation; usually improves with surgery or hearing aids.
- Mixed Hearing Loss: Combination of conductive and sensorineural components.
- Bone Hearing Loss: Often measured during audiometric testing to determine the extent of stapes involvement.
Early diagnosis through hearing tests is crucial for planning effective treatment.
Diagnosis of Otosclerosis
Diagnosis involves a combination of clinical evaluation and hearing tests:
- Physical Examination: ENT specialists check for eardrum abnormalities and other signs.
- Hearing Tests:
- Pure Tone Audiometry measures air and bone conduction to assess the type and severity of hearing loss.
- Tympanometry evaluates middle ear function.
- ABR/ASSR Tests help assess nerve pathways in the inner ear.
- Pure Tone Audiometry measures air and bone conduction to assess the type and severity of hearing loss.
- Imaging: CT scans may be used to visualize bone changes around the stapes.
Proper diagnosis ensures the selection of the most appropriate management strategy, whether surgical or non-surgical.
Treatment Options for Otosclerosis
Treatment depends on the severity of hearing loss and lifestyle needs. Options include:
1. Hearing Aids
For mild to moderate hearing loss, amplification devices can improve hearing:
Hearing aids help bypass the immobile stapes and improve sound clarity in daily life.
2. Otosclerosis Surgery (Stapedectomy or Stapedotomy)
Surgical intervention is the definitive treatment for significant stapes fixation:
- Stapedectomy: Removal of the affected stapes bone and replacement with a prosthetic.
- Stapedotomy: Creating a small hole in the stapes and inserting a prosthesis to restore sound conduction.
Surgery is typically performed by ENT specialists and can restore hearing levels to near normal in many patients.
3. Cochlear Implants
In rare cases of advanced or mixed hearing loss, a cochlear implant may be recommended to bypass damaged structures entirely.
Living with Otosclerosis
- Regular hearing evaluations help monitor progression.
- Protect your ears from excessive noise.
- Maintain follow-up care after otosclerosis surgery or hearing aid fitting.
- Discuss treatment options with ENT specialists and audiologists to find the best personalized approach.
Conclusion
Otosclerosis is a progressive condition that primarily affects the middle ear and stapes, causing bone hearing loss. Recognizing otosclerosis symptoms early and seeking professional evaluation is crucial for preserving hearing. Treatment options range from hearing aids to otosclerosis surgery and, in severe cases, cochlear implants. With proper diagnosis, timely intervention, and ongoing follow-up at clinics like The Hearing Centre Singapore, patients can effectively manage hearing loss, improve quality of life, and prevent long-term complications.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Yes. Otosclerosis often runs in families, making a family history a strong risk factor. Early screening is recommended for relatives, as detecting changes sooner can help manage hearing loss before it worsens.
Early signs typically include gradual hearing loss, difficulty following conversations in noisy places, and ringing or buzzing in the ears (tinnitus). Some people may also notice a sensation of fullness in the ear.
Without timely treatment, bone hearing loss can progress. This may lead to significant hearing impairment over time, affecting daily communication and quality of life.
Stapes fixation occurs when the stapes bone becomes immobile due to abnormal bone growth. This blocks sound transmission to the inner ear, leading to conductive hearing loss that can gradually worsen.
Surgical procedures such as stapedectomy or stapedotomy are highly effective, often restoring hearing close to normal. Success rates are high, and most patients experience significant improvement in hearing clarity.
For mild to moderate hearing loss, modern hearing aids like Signia or Phonak can provide excellent sound amplification. They improve speech clarity and help manage everyday hearing challenges.
Otosclerosis rarely affects balance, but in some cases, if the inner ear is involved, mild dizziness or unsteadiness may occur. Hearing loss remains the primary symptom in most patients.
Otosclerosis commonly develops in adults between 20–50 years old, though hereditary cases can appear earlier. Early diagnosis is important to slow progression and preserve hearing.
There is no medical cure for otosclerosis, but it can be effectively managed. Surgical options like stapedectomy, along with modern hearing aids, help restore hearing and improve quality of life.
Yes. Even a gradual hearing loss warrants professional evaluation. Specialists at The Hearing Centre Singapore can perform detailed hearing tests, identify the cause, and recommend the best treatment for your condition.

Evlin is passionate about helping people with hearing loss. With years of experience in audiology, she has diagnosed and treated a wide range of hearing conditions across all age groups. She is accredited to conduct comprehensive hearing assessments and provide treatments for patients from newborns to the elderly. Committed to personalized care, she strives to empower patients to fully engage in life with better hearing.
Designation: Clinical Audiologist
Qualification: Bachelor of Health Science (Honours) (Audiology), University of Science Malaysia
Membership: .Society of Audiology Professionals in Singapore (SAPS)