Table of Contents
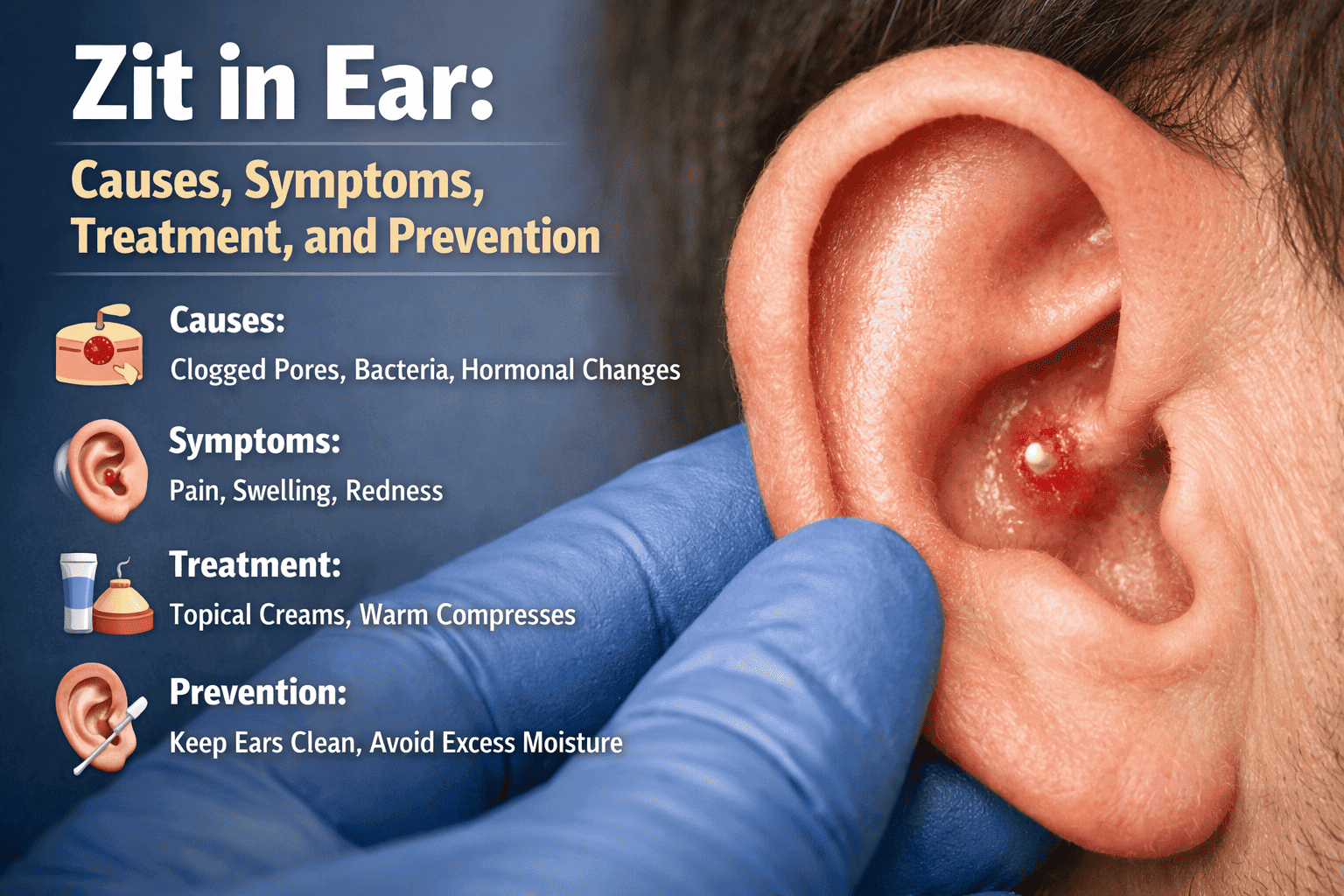
A zit in the ear can be uncomfortable, irritating, and sometimes worrying—especially when it becomes painful or hard to see. Many people experience ear pimples at least once in their lives, yet few understand why they happen or how to treat them safely. This detailed guide explains everything you need to know about a zit in the ear, from common causes and symptoms to treatment options and prevention tips.
Whether you are dealing with a small ear zit, a painful zit, or recurring acne in the ear, this article will help you understand what is happening and what you should do next.
What Is a Zit in the Ear?
A zit in the ear is essentially a blocked pore or infected hair follicle that forms inside or around the ear. Just like pimples on the face or back, ear zits develop when oil, dead skin cells, bacteria, or sweat clog the pores. The Hearing Centre offers specialized ear health services.
A pimple in the ear may appear:
- On the outer ear
- Inside the ear canal
- Behind the ear
- At the ear opening
Because the skin in and around the ear is sensitive, even a small clogged pore can feel extremely uncomfortable.
Common Causes of a Zit in the Ear
Understanding the cause of an ear zit can help prevent future breakouts. The Hearing Centre provides comprehensive ear assessments.
1. Clogged Pores
A clogged pore ear issue is one of the most common reasons for ear acne. Oil, sweat, and dead skin can build up, especially if the ears are not cleaned properly.
2. Bacterial Infection
Bacteria can enter tiny cracks in the skin caused by scratching, earphones, or hearing test, leading to inflammation and infection
3. Excess Oil Production
People with oily skin are more prone to acne, including acne in the ears. Excess oil easily traps dirt and bacteria.
4. Earphones and Headphones
Using earphones for long hours can trap moisture and bacteria inside the ear canal. Dirty earbuds are a frequent cause of recurring ear pimples. A pure tone audiometry test can assess any related hearing impact.
5. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, or stress can trigger acne in unusual areas, including the ears.
6. Poor Ear Hygiene
Infrequent cleaning or aggressive cleaning with cotton buds can push debris deeper into the ear, increasing the risk of pimples.
Types of Ear Zits You May Experience
Not all ear pimples are the same. Identifying the type helps determine the right treatment. Tympanometry measures middle ear pressure.
Small Ear Zit
A small ear zit usually feels like a tiny bump and may not cause much pain. These often resolve on their own within a few days.
Painful Zit
A painful zit in the ear often indicates infection or deep inflammation. Pain may worsen when touching the ear or lying on one side.
Whitehead or Pus-Filled Pimple
This type contains visible white or yellow pus and should never be popped, especially inside the ear.
Blackhead
Blackheads occur when a clogged pore is exposed to air, turning the oil dark. These are more common on the outer ear.
Cystic Acne
Deep, painful lumps may indicate cystic acne, which requires medical attention.
Symptoms of a Zit in the Ear
Common symptoms include:
- Tenderness or pain
- Swelling
- Redness
- A feeling of fullness in the ear
- Discomfort when chewing or talking
- Temporary hearing discomfort if swelling blocks the ear canal
If symptoms worsen or last longer than a week, medical advice is recommended.
Is a Zit in the Ear Dangerous?
Most ear zits are harmless and heal naturally. However, complications can occur if:
- The zit is popped
- Infection spreads
- Severe pain or fever develops
Because the ear canal is close to sensitive structures, untreated infections can sometimes worsen.
How to Treat a Zit in the Ear Safely
1. Do Not Pop It
Popping a pimple in the ear can push bacteria deeper and increase infection risk.
2. Warm Compress
Apply a clean warm compress to the outer ear for 10–15 minutes, two to three times daily. This helps reduce pain and encourages healing.
3. Keep the Area Clean
Gently clean the outer ear with mild soap and water. Avoid inserting anything into the ear canal.
4. Over-the-Counter Treatments
Mild acne creams may be used only on the outer ear—not inside the ear canal.
5. Pain Relief
Over-the-counter pain relievers can help manage discomfort if needed
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical help if:
- Pain becomes severe
- Swelling spreads
- Pus continues to drain
- Hearing is affected
Home Remedies for Ear Zits
Some gentle home remedies may help mild cases:
- Warm compresses
- Keeping ears dry
- Avoiding earphones temporarily
Avoid using essential oils or harsh substances inside the ear. If symptoms persist, diagnostic services such as pure-tone-audiometry-test may be recommended by hearing professionals.
How to Prevent Zits in the Ear
Prevention is often easier and less painful than treatment. Small daily habits can greatly reduce the chances of ear breakouts.
Maintain Ear Hygiene
Clean only the outer ear gently using a soft cloth. Avoid inserting objects into the ear, as this can irritate the skin and push bacteria inside.
Clean Earphones Regularly
Earbuds collect oil, sweat, and dirt over time. Wipe them with a disinfectant cloth at least once a week to reduce bacteria buildup.
Avoid Touching Your Ears
Frequent touching transfers germs from your hands to your ears. This can block pores and increase the risk of pimples forming.
Manage Oily Skin
Excess oil can clog pores around the ear area. Use gentle skincare products that help balance oil without drying the skin.
Reduce Sweat Build-Up
Sweat creates a moist environment where bacteria grow easily. After exercise or long outdoor exposure, clean and dry your ears properly.
Conclusion
A zit in the ear is usually a minor issue, but it can feel more painful due to the sensitive area. With proper care, hygiene, and patience, most ear pimples heal on their own. Avoid popping, keep the area clean, and seek medical help if symptoms worsen.
By maintaining good ear hygiene and a balanced lifestyle, you can reduce the chances of recurring acne in your ears and enjoy better overall comfort.
Frequently Asked Questions:
A zit in the ear usually forms when pores become blocked by oil, sweat, or dead skin. Bacteria can grow in this trapped area, leading to swelling and redness.
Most ear pimples are not dangerous and heal on their own. However, if the area becomes very painful, swollen, or starts leaking fluid, it may indicate infection.
Popping an ear zit is not recommended because it can push bacteria deeper into the skin. This increases the risk of infection and may slow healing.
In most cases, an ear zit clears within a few days to one week. Healing may take longer if the area is irritated or repeatedly touched.
The skin in the ear is thin and sensitive, with little space for swelling. Even a small pimple can cause pressure and sharp discomfort.
Yes, unclean earphones can trap dirt, oil, and moisture in the ear area. Frequent use without cleaning increases the chance of bacterial buildup.
Acne creams should not be applied deep inside the ear canal. If used at all, they should only be applied carefully to the outer ear skin.
You should seek medical help if pain increases, swelling spreads, pus appears, or hearing feels affected. These signs may suggest infection.
Stress can increase oil production and weaken skin defences. This makes breakouts more likely, including in less common areas like the ear.
Keeping ears clean, washing earphones regularly, and avoiding frequent touching can reduce the risk. Good hygiene helps prevent clogged pores.

Evlin is passionate about helping people with hearing loss. With years of experience in audiology, she has diagnosed and treated a wide range of hearing conditions across all age groups. She is accredited to conduct comprehensive hearing assessments and provide treatments for patients from newborns to the elderly. Committed to personalized care, she strives to empower patients to fully engage in life with better hearing.
Designation: Clinical Audiologist
Qualification: Bachelor of Health Science (Honours) (Audiology), University of Science Malaysia
Membership: .Society of Audiology Professionals in Singapore (SAPS)