Table of Contents
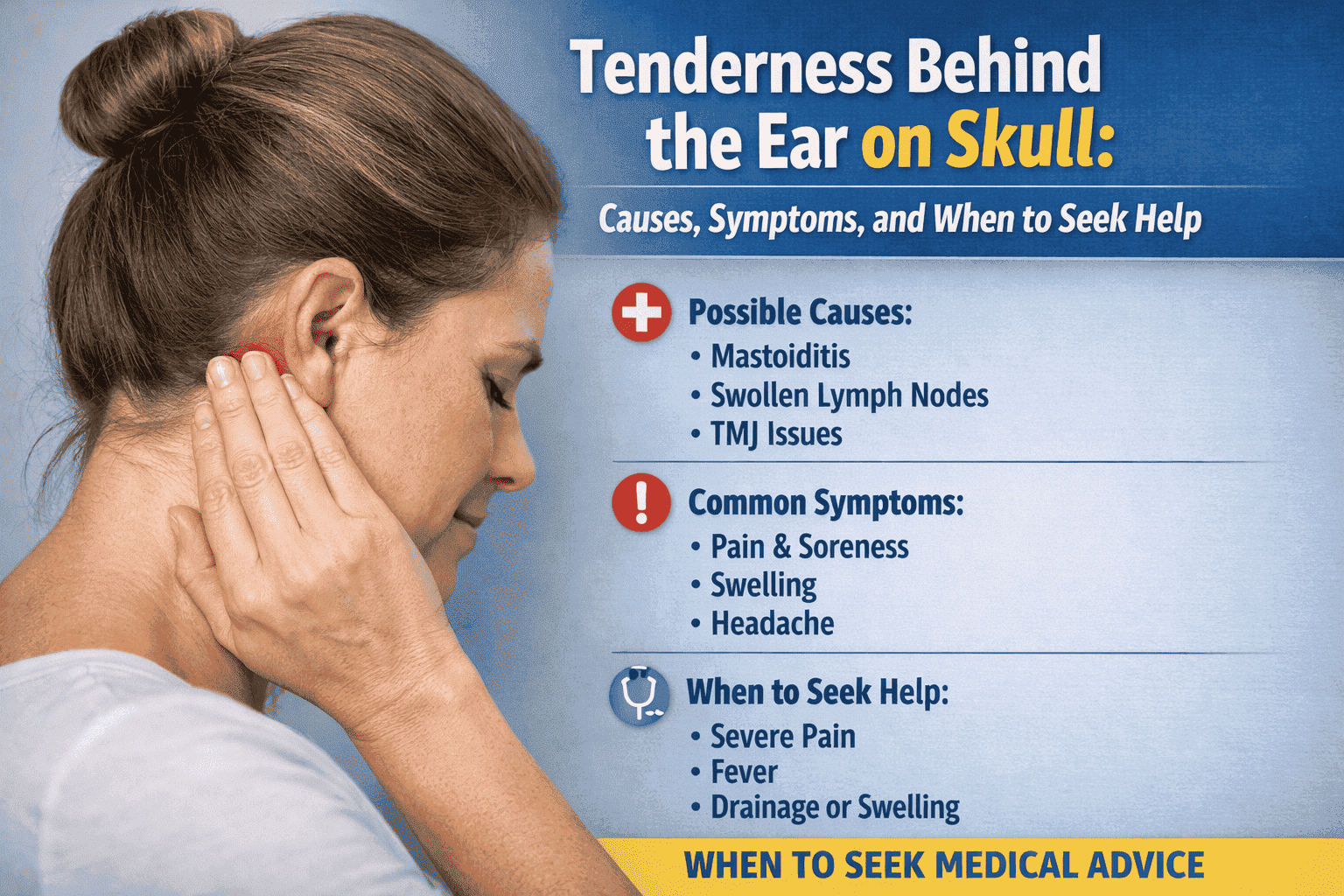
Feeling tenderness behind the ear on the skull can be worrying, especially when the area feels sore to touch or painful when you move your head. Some people notice a dull ache, while others feel sharp pain, swelling, or sensitivity in the bone just behind the ear. This area is medically important because it contains the mastoid bone, muscles, lymph nodes, and nerves that can all contribute to discomfort.
In many cases, tenderness behind the ear is harmless and temporary. However, sometimes it may signal an underlying condition that needs attention. Understanding the possible causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help you decide when to manage it at home and when to see a doctor.
This detailed guide explains everything you need to know about sore behind the ear, skull pain, ear, mastoid tenderness, and related concerns in simple language.
Understanding the Area Behind the Ear
The region contains the mastoid bone with air spaces connected to the middle ear, neck muscles, lymph nodes, and nerves. Mastoid tenderness often signals inflammation here.
Mastoid Bone
Symptoms include pain, touching the bone behind ear, swelling, redness, neck/jaw spread, headaches, or sensitivity to glasses/headphones. Get a hearing test if persistent.
Muscles and Tendons
Neck and scalp muscles attach near the back of the ear. Strain or tension in these muscles can lead to pain and soreness.
Lymph Nodes
Lymph nodes behind the ear help fight infection. When they swell, the area can become tender.
Nerves
Several nerves pass through this region. Irritation or compression can cause pain that feels sharp, burning, or sensitive.
Because so many structures meet in this area, pain can come from many different sources.
Common Symptoms That May Occur
People experience tenderness behind the ear in different ways. Common symptoms include:
- Pain when touching the bone behind the ear
- Swelling or a small lump behind the ear
- Redness or warmth in the area
- Pain that spreads to the neck or jaw
- Headache or pressure near the ear
- Pain that worsens when turning the head
- Sensitivity when wearing glasses or headphones
The severity can range from mild discomfort to intense pain, depending on the cause.
Common Causes of Tenderness Behind the Ear on the Skull
Swollen Lymph Nodes
One of the most common causes of a sore behind ear is swollen lymph nodes. This usually happens when your body is fighting an infection.
- Lymph nodes may swell due to:
- Ear infections
- Throat infections
- Cold or flu
- Skin infections on the scalp
Swollen nodes often feel like small, tender lumps and usually reduce once the infection clears.
Ear Infections
Middle ear or outer ear infections can cause pain that spreads to the skull behind the ear. In some cases, the pain feels deeper and more intense.
- Symptoms may include:
- Ear pain or pressure
- Reduced hearing
- Fluid discharge
- Fever
If untreated, some ear infections can spread and cause more serious issues.
Mastoid Tenderness and Mastoiditis
The mastoid bone can become inflamed or infected, leading to mastoid tenderness. This condition is more common in children but can also affect adults.
- Signs of mastoid-related pain include:
- Persistent pain behind the ear
- Swelling or redness
- Pain that worsens over time
- Fever
Mastoiditis is a medical condition that requires prompt treatment.
Muscle Strain and Tension
Muscle tension is a very common reason for skull pain ear. Poor posture, stress, or sleeping in an awkward position can strain neck and scalp muscles.
Common triggers include:
- Long hours at a desk
- Using mobile phones frequently
- Sleeping without proper neck support
- Stress and anxiety
This type of pain usually improves with rest and posture correction.
Bone Pain Behind Ear
Bone pain ear can feel deep, aching, or sharp. It may come from inflammation, injury, or pressure on the skull bone.
Possible causes include:
- Minor head injury
- Repeated pressure from tight headgear
- Inflammation of the surrounding tissues
Bone pain should not be ignored if it persists or worsens.
Skin and Scalp Conditions
Skin issues around the ear and scalp can also cause tenderness. These conditions usually lead to localized pain, swelling, or sensitivity.
Common examples include:
- Boils or abscesses behind the ear
- Infected hair follicles on the scalp
- Sebaceous cysts
- Allergic reactions to hair products or accessories
These conditions often cause redness, warmth, and discomfort when touched.
Nerve-Related Pain
Irritation or compression of nearby nerves can lead to sharp or burning pain behind the ear.
This type of pain may:
- Come suddenly without warning
- Feel electric, stabbing, or shooting
- Worsens when the area is touched or pressed
Nerve-related pain often requires medical evaluation to identify the exact cause and rule out underlying conditions.
When Is Tenderness Behind the Ear on Skull a Concern?
While many causes are mild and temporary, some warning signs should not be ignored.
Seek medical advice if:
- Pain lasts more than a few days
- Pain is severe or getting worse
- There is noticeable swelling, redness, or warmth
- You experience fever or chills
- There is hearing loss or fluid discharge from the ear
- Pain follows a head injury or trauma
Early diagnosis helps prevent complications and ensures proper treatment
How Doctors Diagnose the Problem
To identify the cause of tenderness behind the ear, a doctor may:
- Exam, history, lymph checks, hearing assessments, and imaging. Ear measurements aid evaluation.
- Examine the ear, scalp, neck, and skull area
- Check for swollen or tender lymph nodes
- Assess hearing and ear function
- Recommend imaging tests if needed
Diagnosis depends on symptom duration, severity, and physical findings.
Treatment Options for Tenderness Behind Ear
Home Care for Mild Pain
If symptoms are mild, simple home care can help reduce discomfort.
Helpful steps include:
- Applying a warm compress to ease pain
- Resting the neck and avoiding strain
- Maintaining good posture during daily activities
- Avoiding pressing, rubbing, or massaging painful lumps
- Staying well hydrated
Mild pain often improves within a few days with proper care.
Medical Treatment
If the cause involves infection or inflammation, treatment may include:
- Medications to reduce inflammation
- Treatment for ear, skin, or scalp infections
- Pain relief as advised by a healthcare professional
Always follow medical guidance and avoid self-medication.
Managing Muscle-Related Pain
For pain caused by muscle tension, the following steps may help:
- Gentle neck and shoulder stretches
- Using a supportive pillow while sleeping
- Taking regular breaks from screens and devices
- Practising stress management techniques
Consistency with these habits is important for long-term relief.
Can Tenderness Behind the Ear Be Prevented?
Although not all causes can be prevented, certain habits can lower your risk.
Preventive measures include:
- Treating ear infections early
- Maintaining good ear and scalp hygiene
- Avoiding prolonged poor posture
- Using comfortable headgear and eyewear
- Managing stress effectively
Small lifestyle changes can make a noticeable difference over time.
Living With a Sensitive Area Behind the Ear
A sensitive area behind the ear can affect daily comfort, especially when wearing glasses, headphones, helmets, or sleeping on one side. Identifying triggers and reducing pressure on the area can help manage symptoms until healing occurs.
Conclusion
Tenderness behind the ear from muscle strain to mastoiditis resolves mildly at home, but see The Hearing Centre for persistent mastoid tenderness or bone pain ear. While mild soreness behind the ear often resolves on its own, persistent or severe pain should never be ignored.
By understanding symptoms like sore behind the ear, skull pain ear, mastoid tenderness, and bone pain ear, you can take the right steps toward relief and timely medical care. Paying attention to your body and seeking help when needed ensures better ear and overall health.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Common causes include swollen lymph nodes, ear infections, muscle strain, mastoid inflammation, and skin conditions.
Mild mastoid tenderness may be harmless, but persistent pain or swelling should be checked by a doctor.
Yes, stress can cause muscle tension in the neck and scalp, leading to soreness behind the ear.
This may be due to inflammation, muscle strain, swollen lymph nodes, or minor injury.
Yes, tension headaches and nerve-related pain can cause discomfort near the ear and skull.
Mild pain may last a few days, while pain from infections may last longer if untreated.
Yes, poor sleeping posture or lack of neck support can strain muscles and cause tenderness.
Seek medical help if pain is severe, persistent, or accompanied by fever, swelling, or hearing problems.
They can be tender, especially during infections, and usually improve once the infection resolves.
Yes, ear infections can cause pain that spreads to the skull behind the ear.

Evlin is passionate about helping people with hearing loss. With years of experience in audiology, she has diagnosed and treated a wide range of hearing conditions across all age groups. She is accredited to conduct comprehensive hearing assessments and provide treatments for patients from newborns to the elderly. Committed to personalized care, she strives to empower patients to fully engage in life with better hearing.
Designation: Clinical Audiologist
Qualification: Bachelor of Health Science (Honours) (Audiology), University of Science Malaysia
Membership: .Society of Audiology Professionals in Singapore (SAPS)