Table of Contents
The eardrum (tympanic membrane) vibrates to transmit sound but can tear from infections, pressure, or injury, causing ear drum damage symptoms like pain or hearing loss. Early detection via hearing test prevents complications. When the eardrum is damaged, hearing can be affected, and discomfort or complications may occur.
Understanding ear drum damage symptoms is important because early detection can prevent long-term hearing problems. Many people ignore mild symptoms, thinking they will go away on their own. However, untreated eardrum damage can lead to infections, hearing loss, and balance issues.
This guide explains ear drum damage symptoms in detail, including early warning signs, severe symptoms, causes, risk factors, and treatment options. The information is written in simple, easy-to-understand language so anyone can recognise potential problems and know when to seek professional care.
What Is the Eardrum and Why Is It Important?
This thin membrane separates the outer and middle ear, transmitting sound and protecting from bacteria. Damage risks tympanometry abnormalities.
- It helps transmit sound vibrations to the hearing bones
- It protects the middle ear from bacteria, water, and debris
Because the eardrum is thin and sensitive, it can be damaged easily by infections, pressure changes, loud sounds, or physical injury.
What Is Ear Drum Damage?
Ear drum damage occurs when the tympanic membrane becomes:
- Torn
- Perforated
- Inflamed
- Weakened
Damage can be mild, moderate, or severe. In some cases, the eardrum heals on its own. In others, medical treatment is required to restore hearing and prevent complications.
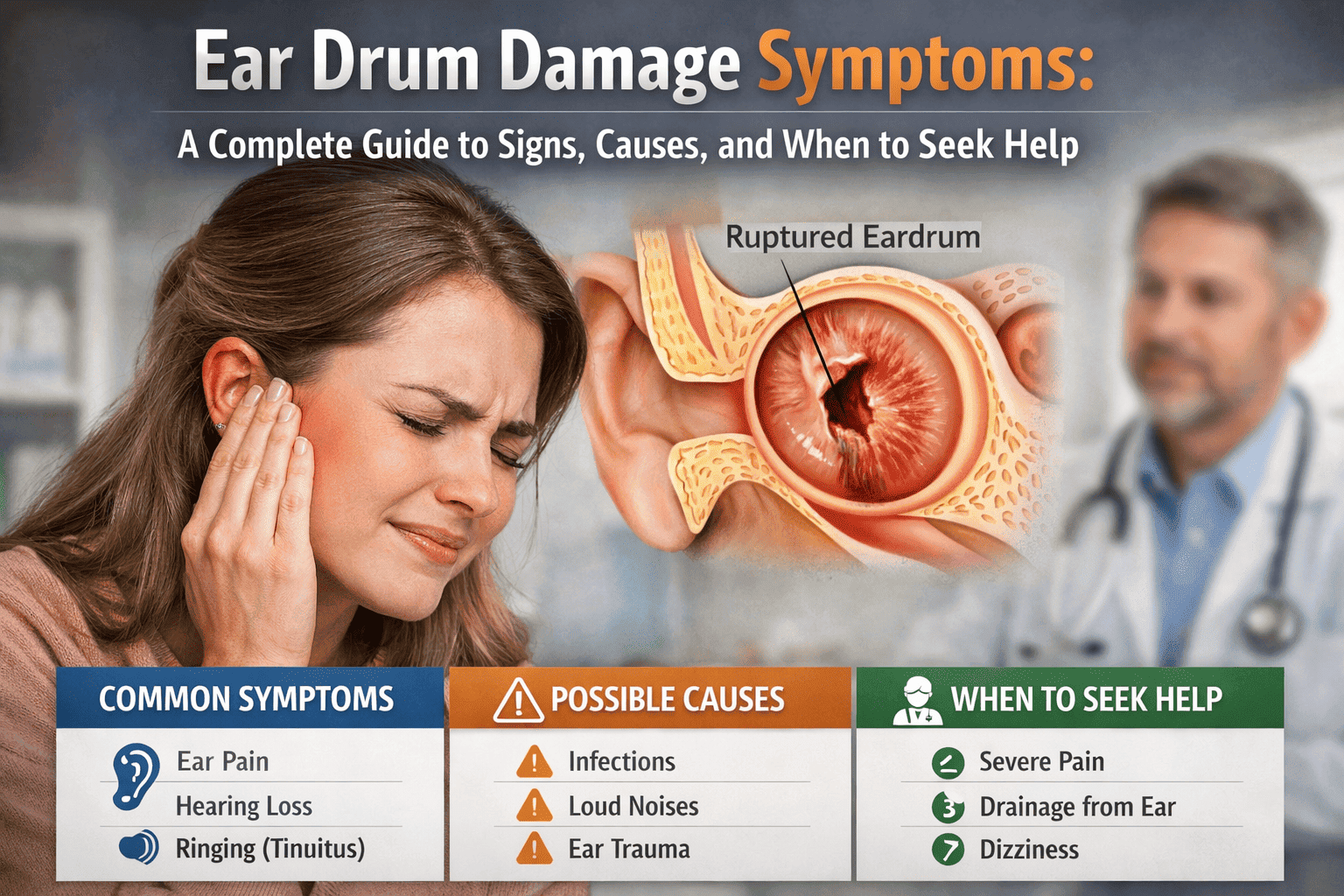
Common Ear Drum Damage Symptoms
Ear drum damage symptoms can vary depending on the cause and severity of the injury. Some symptoms appear suddenly, while others develop gradually.
1. Ear Pain or Discomfort
Sharp/dull pain worsening with yawning; signals middle ear issues.
- Sharp or sudden
- Dull and constant
- Worse when chewing or yawning
In some cases, pain may decrease once the eardrum ruptures, especially during an infection.
2. Hearing Loss or Reduced Hearing
Hearing loss is a key sign of eardrum damage. You may notice:
- Muffled speech needs hearing assessment.
- Difficulty hearing conversations
- Needing higher volume on devices
The hearing loss can be temporary or permanent, depending on the extent of the damage.
3. Ringing or Buzzing in the Ear
Ringing in the ear, also known as tinnitus, is another common symptom. People often describe it as:
- Buzzing
- Ringing
- Humming
Tinnitus can be mild or constant and may worsen in quiet environments.
4. Fluid or Discharge from the Ear
Fluid leaking from the ear is a serious sign of eardrum damage. The discharge may be:
- Clear
- Yellow or white
- Bloody
Discharge often indicates infection or a perforated eardrum and should never be ignored.
5. Sensation of Fullness or Pressure
Many people with eardrum damage experience a feeling of:
- Pressure inside the ear
- Blockage
- Fullness that does not clear
This sensation may worsen during altitude changes or colds.
6. Dizziness or Balance Problems
Because the ear plays a role in balance, eardrum damage may cause:
- Dizziness
- Vertigo
- Unsteadiness while walking
These symptoms can interfere with daily activities and increase the risk of falls.
- Increased Sensitivity to Sound
Sound sensitivity, bleeding, infections, and fever require cochlear implant evaluation if severe. This happens because the damaged eardrum does not regulate sound properly.
8. Ear Bleeding
Bleeding from the ear can occur if the eardrum is torn due to trauma or pressure changes. Even small amounts of blood should be taken seriously.
9. Recurrent Ear Infections
A damaged eardrum makes it easier for bacteria to enter the middle ear. Frequent ear infections can be both a cause and a symptom of eardrum damage.
10. Fever and General Discomfort
When infection is present, ear drum damage symptoms may also include:
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Headache
These symptoms suggest that medical attention is needed.
Early vs Severe Ear Drum Damage Symptoms
Early Symptoms
- Mild ear pain
- Slight hearing difficulty
- Occasional ringing
- Ear pressure
Early symptoms are often overlooked but should still be evaluated.
Severe Symptoms
- Noticeable hearing loss
- Persistent discharge
- Severe pain or dizziness
- Bleeding from the ear
Severe symptoms require prompt medical care to avoid complications.
Common Causes of Ear Drum Damage
Understanding the cause helps explain why ear drum damage symptoms develop.
Ear Infections
Middle ear infections are one of the most common causes. Pressure from fluid buildup can rupture the eardrum.
Loud Noise Exposure
Sudden loud sounds, such as explosions or very loud music, can damage the eardrum.
Physical Injury
Inserting objects into the ear, accidental blows, or head injuries can tear the eardrum.
Pressure Changes
Sudden pressure changes during flying, diving, or driving in mountains can cause barotrauma.
Improper Ear Cleaning
Using cotton buds or sharp objects can easily damage the delicate membrane.
Who Is at Higher Risk of Ear Drum Damage?
Certain groups are more vulnerable:
- Children with frequent ear infections
- Swimmers and divers
- People exposed to loud noise
- Individuals who clean ears aggressively
- Those with untreated colds or sinus infections
Awareness helps reduce risk and encourage early treatment.
How Ear Drum Damage Affects Hearing
The eardrum is essential for sound transmission. When damaged:
- Sound vibrations are weakened
- Speech clarity decreases
- Background noise becomes harder to filter
Even small tears can affect hearing quality.
Diagnosis of Ear Drum Damage
Doctors diagnose eardrum damage through:
- Physical ear examination
- Otoscope inspection
- Hearing tests
- Imaging in severe cases
Early diagnosis improves recovery outcomes.
Treatment Options for Ear Drum Damage
Natural Healing
Small tears often heal within weeks without intervention.
Medication
Antibiotics may be prescribed if infection is present.
Ear Protection
Keeping the ear dry and avoiding pressure changes supports healing.
Surgical Repair
Severe or long-lasting damage may require a procedure called tympanoplasty.
Can Ear Drum Damage Heal on Its Own?
Yes, many cases heal naturally. However, healing depends on:
- Size of the tear
- Cause of damage
- Presence of infection
Medical monitoring ensures proper recovery.
How to Prevent Ear Drum Damage
Prevention plays a key role in ear health:
- Avoid inserting objects into the ear
- Protect ears from loud noise
- Treat ear infections early
- Use ear protection when swimming
- Be careful during air travel
Simple habits can significantly reduce risk.
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical help if you experience:
- Persistent ear pain
- Hearing loss
- Ear discharge or bleeding
- Dizziness or balance problems
Early treatment prevents complications and hearing loss.
Long-Term Complications of Untreated Ear Drum Damage
If ignored, eardrum damage can lead to:
- Chronic ear infections
- Permanent hearing loss
- Middle ear damage
- Balance disorders
Prompt care protects long-term hearing health.
Conclusion
Spot ear drum damage symptoms early to avoid hearing loss; professional hearing test ensures care. While some symptoms are mild, others indicate urgent medical issues. Ear pain, hearing loss, ringing, discharge, or dizziness should never be ignored.
Healthy ears are essential for communication, balance, and quality of life. If you notice any changes in your hearing or ear comfort, professional evaluation is always the safest choice.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Common symptoms include ear pain, hearing loss, ringing, discharge, and a feeling of pressure in the ear.
Yes, severe or untreated damage can lead to permanent hearing loss.
Yes, tinnitus can occur when the eardrum is damaged.
Not always. Some people experience hearing loss or discharge without significant pain.
Minor damage may heal within a few weeks, while severe damage may take longer.
Yes, repeated or severe ear infections are a common cause of eardrum damage.
Yes, keeping the ear dry helps prevent infection and supports healing.
Sudden or extreme noise exposure can injure the eardrum and inner ear.
Ear bleeding often indicates trauma or rupture and should be checked by a doctor.
You should see a doctor if symptoms persist, worsen, or include hearing loss, discharge, or dizziness.

Evlin is passionate about helping people with hearing loss. With years of experience in audiology, she has diagnosed and treated a wide range of hearing conditions across all age groups. She is accredited to conduct comprehensive hearing assessments and provide treatments for patients from newborns to the elderly. Committed to personalized care, she strives to empower patients to fully engage in life with better hearing.
Designation: Clinical Audiologist
Qualification: Bachelor of Health Science (Honours) (Audiology), University of Science Malaysia
Membership: .Society of Audiology Professionals in Singapore (SAPS)