Table of Contents
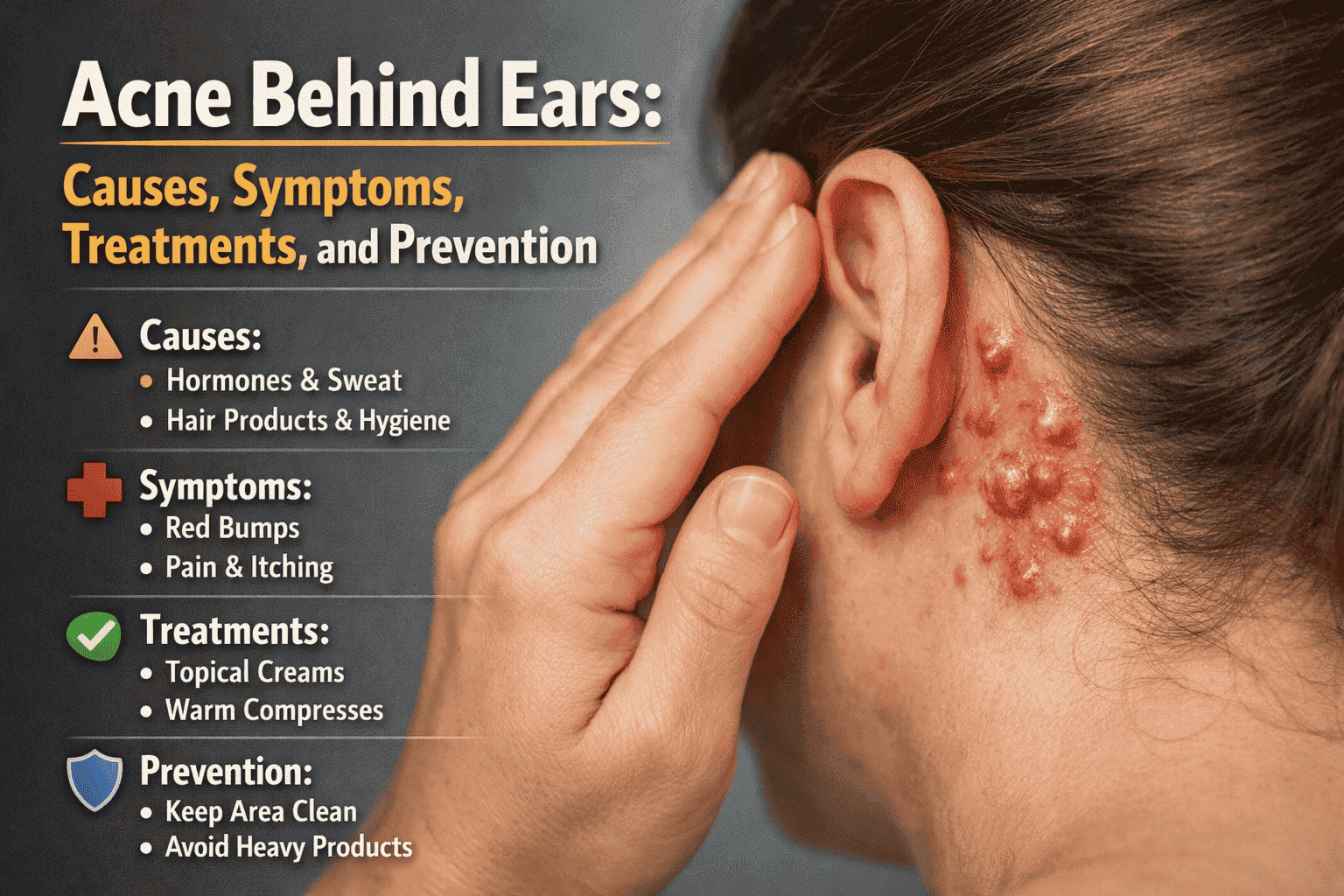
Acne is a common skin issue, but when it appears in less visible areas like behind the ears, it can be uncomfortable, painful, and confusing. Many people suffer from pimples behind the ears, zits behind the ears, or acne near the ears without understanding the causes, treatment, or prevention strategies. This comprehensive guide explains everything you need to know about acne behind the ears, including causes, symptoms, treatment options, lifestyle tips, and prevention strategies.
Whether you are dealing with a small skin bump or a painful acne ear, this article offers detailed insights and solutions to manage and prevent acne effectively.
What Is Acne Behind Ears?
Acne behind the ears refers to clogged pores or infected hair follicles that appear in the area behind the ear or around the earlobe. Like facial acne, these skin bumps form due to excess oil, dead skin cells, and bacterial growth. The skin behind the ear is sensitive, making these zits often painful and prone to irritation.
This type of acne can appear as:
- Small red bumps
- Pus-filled zits
- Tender lumps
- Skin irritation with mild swelling
While often not dangerous, painful acne can impact daily comfort, especially when wearing headphones, hats, or glasses.
Causes of Acne Behind Ears
Understanding the causes is crucial for effective treatment and prevention.
1. Clogged Pores
A clogged pore is the primary cause of a zit behind the ear. Oil, sweat, and dirt can accumulate, especially if the area is not cleaned regularly.
2. Excess Oil Production
Oily skin types are more prone to developing acne behind the ears. Excess sebum production can trap debris and bacteria.
3. Bacterial Infection
Bacteria from hands, hair products, or contaminated surfaces can infect pores, leading to painful acne ears.
4. Sweat and Moisture
Sweat accumulation from workouts or humid weather can contribute to skin bumps and pimples in hidden areas.
5. Hair Products and Styling
Shampoos, conditioners, hair gels, and sprays can leave residues that irritate the skin behind the ears and block pores.
6. Hormonal Changes
Fluctuations in hormones during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, or stress can trigger acne flare-ups in unusual areas like behind the ears.
7. Friction and Pressure
Constant friction from hats, headphones, or masks can worsen existing pimples or create new skin bumps behind the ears.
Types of Acne Behind Ears
Not all acne behind the ears is the same. Identifying the type helps in choosing the right treatment.
Small Skin Bumps
These are tiny red or flesh-colored bumps that are usually painless and may resolve naturally.
Pustules or Pus-Filled Zits
These zits have white or yellow pus and are often tender. Avoid squeezing to prevent infection.
Cystic Acne
Deep, painful lumps that may persist for weeks and require medical attention.
Blackheads
Blackheads may appear if a clogged pore is exposed to air, turning the oil dark.
Nodules
Hard, painful lumps deep under the skin, which can cause long-term scarring if untreated.
Symptoms of Acne Behind Ears
Common symptoms include:
- Redness and inflammation
- Tenderness or pain
- Swelling behind the ear
- Pus or discharge from severe pimples
- Itchiness or discomfort
- Irritation when wearing hats, glasses, or headphones
Treatment Options for Acne Behind Ears
1. Keep the Area Clean
Gently wash the area with mild, non-comedogenic soap. Avoid harsh scrubbing.
2. Avoid Popping Pimples
Do not squeeze or pop pimples behind the ears, as this can spread bacteria and worsen infection.
3. Topical Treatments
Over-the-counter creams containing benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid can help reduce acne. Apply only to the affected area.
4. Warm Compress
A warm compress can reduce inflammation and promote natural drainage of pus from small zits.
5. Pain Management
For painful acne ear, over-the-counter pain relief can alleviate discomfort.
6. Professional Care
Seek medical attention for severe or persistent acne. Dermatologists can prescribe antibiotics or other treatments for cystic acne.
7. Check for Ear or Skin Conditions
If the acne is recurrent or accompanied by hearing discomfort, a professional ear evaluation may be helpful. Services like hearing-test or tympanometry can assess any underlying ear issues.
Home Remedies for Acne Behind Ears
Gentle home care can help mild cases:
- Warm compresses for 10–15 minutes daily
- Avoiding oily hair products
- Keeping the area dry and clean
- Using non-comedogenic skincare
Note: Avoid inserting any substances into the ear canal. Persistent issues may require testing, like pure-tone-audiometry-test to rule out infections affecting hearing.
Prevention Tips
Maintain Hygiene
Clean behind the ears daily and after sweating.
Reduce Friction
Limit the use of hats or headphones that press on the area.
Avoid Oily Hair Products
Use lightweight, non-comedogenic hair products.
Manage Stress and Hormones
A balanced lifestyle and stress management can reduce hormonal triggers.
Healthy Diet
A diet rich in fresh fruits, vegetables, and minimal processed foods supports overall skin health.
Monitor for Ear Health
Persistent skin bumps accompanied by pain or hearing issues should prompt consultation with hearing specialists, such as cochlear-implant or hearing-implant.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Better Skin Health
- Shower after workouts to remove sweat and bacteria
- Change pillowcases and hats regularly
- Avoid touching or scratching the affected area
- Maintain hydration and balanced nutrition
Early attention to skin and ear health prevents severe acne and reduces risk of infection.
When to See a Doctor
Consult a healthcare provider if:
- Acne behind the ears is persistent or recurrent
- There is severe pain, swelling, or pus
- Acne leads to scarring
- Hearing discomfort or other ear symptoms appear
Advanced diagnostics, including abr-assr, help rule out underlying ear conditions.
Conclusion
Acne behind the ears is a common but manageable skin concern. With proper hygiene, careful skincare, lifestyle adjustments, and timely professional care, most cases can be resolved without complications. Paying attention to both skin and ear health ensures comfort, reduces pain, and prevents long-term issues.
By following prevention strategies, monitoring symptoms, and consulting specialists when necessary, you can keep your skin healthy while protecting your hearing.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Acne behind the ears can develop due to clogged pores, bacterial buildup, excess oil production, friction from clothing or accessories, and hormonal changes.
Treatment involves gently cleaning the area, applying topical acne treatments, using warm compresses to reduce inflammation, and avoiding popping to prevent infection or scarring.
Some pimples are mild and barely noticeable, but larger or cystic acne can cause tenderness, swelling, and discomfort.
Yes, prolonged use of headphones can trap sweat and bacteria, and friction from ear pads or straps may contribute to pimples forming.
You should consult a doctor if the acne is persistent, painful, filled with pus, spreads rapidly, or begins to affect nearby areas like the ear canal.
Home care can help mild cases: gently cleanse the area daily, use warm compresses, keep the region dry, and avoid applying harsh or oily products.
Diet can play a supportive role; a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and adequate hydration helps maintain overall skin health, though it is rarely the sole cause.
Popping is not recommended. It can push bacteria deeper, increase inflammation, and cause scarring, making healing slower.
Prevention includes regular hygiene, avoiding excessive touching, keeping hair and accessories clean, using non-comedogenic skincare products, and managing stress effectively.
Yes, sometimes infections can mimic or worsen acne, causing swelling, redness, or tenderness in the area around the ear.

Evlin is passionate about helping people with hearing loss. With years of experience in audiology, she has diagnosed and treated a wide range of hearing conditions across all age groups. She is accredited to conduct comprehensive hearing assessments and provide treatments for patients from newborns to the elderly. Committed to personalized care, she strives to empower patients to fully engage in life with better hearing.
Designation: Clinical Audiologist
Qualification: Bachelor of Health Science (Honours) (Audiology), University of Science Malaysia
Membership: .Society of Audiology Professionals in Singapore (SAPS)