Table of Contents
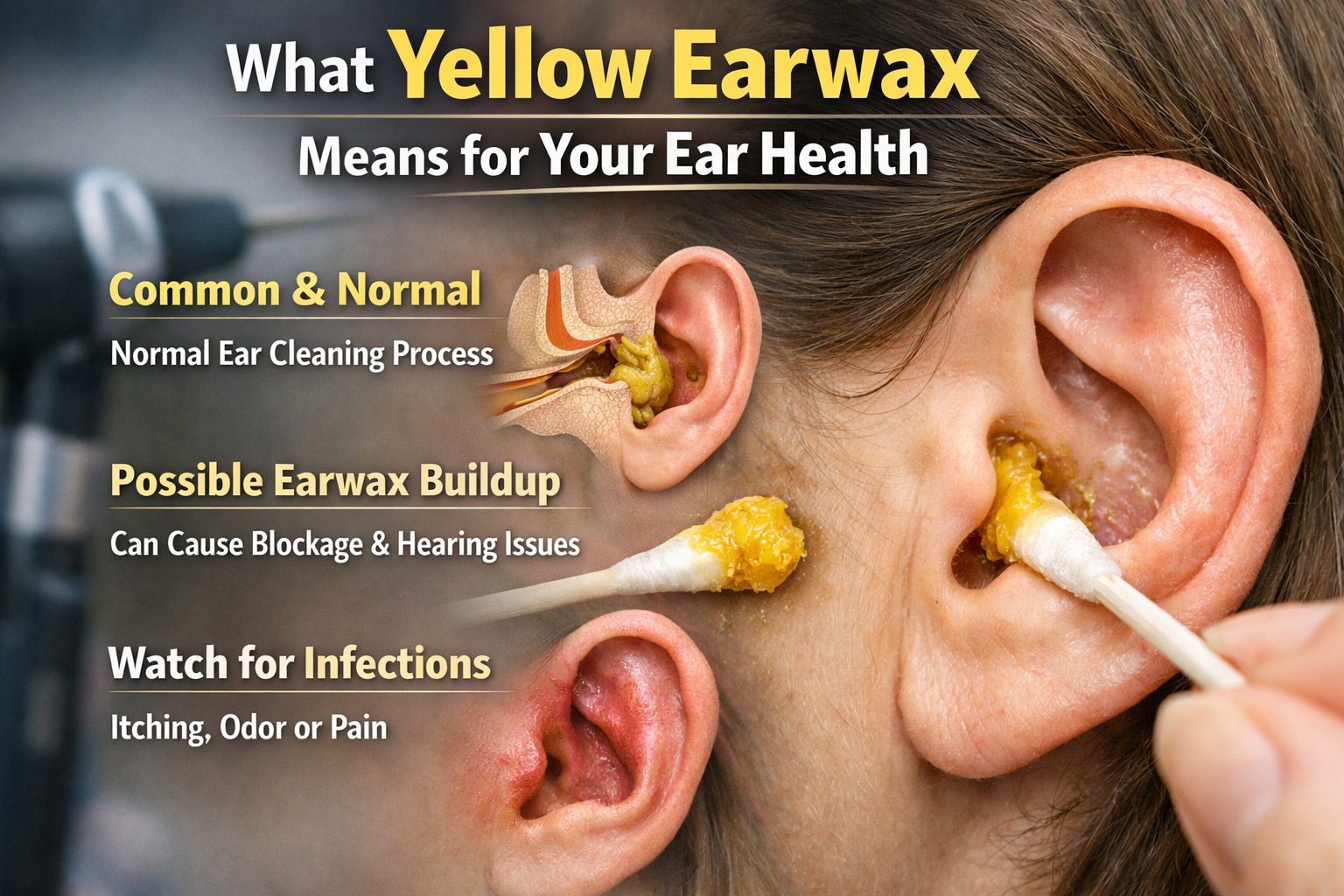
Earwax, also called cerumen, is a natural substance produced by glands in the ear canal. It helps protect the ear from dust, bacteria, and other foreign particles. The appearance of yellowish discharge or soft wax is usually normal, but changes in color, consistency, or amount can sometimes indicate underlying ear conditions.
Understanding the types of earwax, its function, and proper ear hygiene is essential to maintain ear health. In this blog, we explore everything about yellow earwax, from causes and variations to safe cleaning methods, and when it is time to consult a professional. At The Hearing Centre, they offer comprehensive assessments.
What is Earwax?
Earwax, or cerumen, is a sticky substance secreted by ceruminous and sebaceous glands in the ear canal. Its main roles include:
- Protecting the ear canal from dust, bacteria, and fungi
- Lubricating the ear canal to prevent dryness or irritation
- Trapping small particles before they reach the eardrum
Earwax comes in different colors and textures. Normal wax is usually yellow to brown, soft or sticky, and gradually moves out of the ear naturally. Changes in color or texture may indicate hygiene issues, infection, or other conditions. Hearing tests can evaluate related concerns.
Types of Yellow Ear Wax
Yellow ear wax can vary in shade, texture, and consistency:
- Soft yellow wax: Usually normal, slightly sticky, and easy to remove naturally
- Sticky yellow wax: Can accumulate if ear hygiene is inadequate
- Bright yellow discharge with odor: Could signal infection or inflammation
- Dark yellow wax: Often older wax that has hardened and moved from the inner ear
Understanding these variations helps distinguish between normal wax and signs of ear problems. Pure tone audiometry test assesses any hearing impact from the buildup.
Causes of Yellow Ear Wax
Yellow earwax is generally normal, but there are several reasons it may appear more noticeable:
Natural Production
Some people naturally produce more wax than others, and it may be yellow due to its composition of secreted oils and dead skin cells.
Ear Hygiene Practices
Cleaning ears too frequently or using cotton swabs improperly can push wax deeper into the ear canal, leading to accumulation and sticky yellow wax. ABR ASSR testing supports the diagnosis of related issues.
Infection or Inflammation
Ear infections may cause yellowish discharge that can be accompanied by a foul smell, pain, or itchiness. Tympanometry measures ear canal pressure accurately.
Skin Conditions
Conditions like eczema in the ear canal can alter wax texture and color, sometimes leading to yellow buildup.
When to Worry About Yellow Ear Wax
Not all yellow wax is concerning, but you should consult a healthcare professional if you notice:
- Persistent ear pain or discomfort
- Hearing loss or muffled sounds
- Foul odor from the ear
- Fever or dizziness
- Yellow discharge mixed with blood or pus
Ignoring these symptoms may lead to complications, such as infections or eardrum damage. Consider cochlear implant options for severe hearing concerns.
How to Maintain Ear Hygiene
Proper ear hygiene prevents wax buildup and keeps ears healthy:
- Avoid cotton swabs deep in the ear: Only clean the outer ear gently
- Use ear drops when recommended: Softens wax for natural removal
- Keep ears dry: Prevents bacterial and fungal growth
- Regular checkups: ENT professionals can safely remove wax if needed
Practising safe ear hygiene ensures that soft wax or sticky yellow wax does not turn into a problem. Hearing implant solutions may help chronic cases. The Hearing Centre provides professional cleanings.
Tips for Healthy Ears
- Avoid inserting foreign objects in the ear
- Keep hair and accessories clean to reduce friction and bacteria
- Manage allergies and sinus problems that can affect ear health
- Schedule routine ear examination if you experience frequent buildup or discomfort
Conclusion
Yellow earwax is usually normal and part of the ear’s natural defence system. Soft wax or sticky yellow wax is common, but changes in color, consistency, or quantity should not be ignored. Maintaining proper ear hygiene, avoiding harmful cleaning practices, and consulting professionals when needed ensures healthy ears and prevents complications. Understanding earwax meaning and practising preventive care can help you maintain optimal ear health and comfort.
Frequently Asked Questions:
It is usually produced naturally, consisting of oils, dead skin, and debris from the ear canal.
Yes, yellow wax is common and protective. Only seek help if accompanied by pain or discharge.
Yes, infections may produce yellow discharge with odor, pain, or itchiness
Use softening drops or consult an ENT specialist; avoid cotton swabs deep in the ear.
Partly. Yellow wax is normal, but unusual colors like green, black, or blood-stained may indicate infection or trauma.
Yes, excess wax can block the ear canal, causing muffled hearing or pressure.
Only clean the outer ear gently. Earwax inside the ear canal usually moves out naturally and doesn’t need to be removed.
Yes, allergies can increase wax production or change its consistency.
Yes, if used as directed; avoid overuse or using drops with unknown ingredients.
See a doctor if yellow wax is persistent, painful, or accompanied by hearing loss, dizziness, or odor.

Evlin is passionate about helping people with hearing loss. With years of experience in audiology, she has diagnosed and treated a wide range of hearing conditions across all age groups. She is accredited to conduct comprehensive hearing assessments and provide treatments for patients from newborns to the elderly. Committed to personalized care, she strives to empower patients to fully engage in life with better hearing.
Designation: Clinical Audiologist
Qualification: Bachelor of Health Science (Honours) (Audiology), University of Science Malaysia
Membership: .Society of Audiology Professionals in Singapore (SAPS)